迫于找工作,不得不一边鄙视自己的智商,一边硬着头皮刷 LeetCode。既然开始刷题,那顺便做个笔记,以便日后温习。
因为顺序是乱的,所以请善用 CTRL-F。
217. Contains Duplicate
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 Input: nums = [1,2,3,1] Output: true Input: nums = [1,2,3,4] Output: false
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean containsDuplicate (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) { return false ; } HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet <>(); for (int i : nums) { if (hashSet.contains(i)) { return true ; } hashSet.add(i); } return false ; } }
242. Valid Anagram
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" Output: true Input: s = "rat", t = "car" Output: false
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { if (s.length() != t.length()) { return false ; } Map<Character, Integer> countS = new HashMap <>(); Map<Character, Integer> countT = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { countS.put( s.charAt(i), countS.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0 ) + 1 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length(); i++) { countT.put( t.charAt(i), countT.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0 ) + 1 ); } return countS.equals(countT); } }
1299. Replace Elements with Greatest Element on Right Side
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Input: arr = [17,18,5,4,6,1] Output: [18,6,6,6,1,-1] Explanation: - index 0 --> the greatest element to the right of index 0 is index 1 (18). - index 1 --> the greatest element to the right of index 1 is index 4 (6). - index 2 --> the greatest element to the right of index 2 is index 4 (6). - index 3 --> the greatest element to the right of index 3 is index 4 (6). - index 4 --> the greatest element to the right of index 4 is index 5 (1). - index 5 --> there are no elements to the right of index 5, so we put -1.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int [] replaceElements(int [] arr) { int max = -1 ; for (int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int a = arr[i]; arr[i] = max; max = Math.max(max, a); } return arr; } }
解题思路就是把 explanation 反过来看,既然要找元素右边最大的数,那么就从最右开始,这样找到的最大的数必定适用于 arr[i] ~ arr[length - 1] 这个范围。
392. Is Subsequence
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Input: s = "abc", t = "ahbgdc" Output: true Input: s = "axc", t = "ahbgdc" Output: false Input: s = "acb", t = "ahbgdc" Output: false Input: s = "aaaaaa", t = "bbaaaa" Output: false
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public boolean isSubsequence (String s, String t) { if (s.equals(t) || s.length() == 0 ) { return true ; } if (t.length() == 0 ) { return false ; } int sIndex = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length(); i++) { if (t.charAt(i) == s.charAt(sIndex)) { sIndex++; if (sIndex >= s.length()) { return true ; } } } return false ; } }
解题思路就是整两个指针,sIndex 指向 s 的各个字符,在循环里面逐个取 t 的字符跟 s[sIndex] 对比,匹配到的话 sIndex 就往下走一步,如果 sIndex 能走到头,就说明 s 是 t 的子序列。
58. Length of Last Word
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Input: s = "Hello World" Output: 5 Explanation: The last word is "World" with length 5. Input: s = " fly me to the moon " Output: 4 Explanation: The last word is "moon" with length 4.
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution { public int lengthOfLastWord (String s) { String[] strs = s.split(" " ); return strs[strs.length - 1 ].length(); } }
我的评价是,这道题不应该出现在 LeetCode,应该出现在大学 Java 课程的作业里。
14. Longest Common Prefix
Example:
1 2 Input: strs = ["flower","flow","flight"] Output: "fl"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) { if (strs.length == 0 ) { return "" ; } String commonPrefix = strs[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < strs.length; i++) { while (strs[i].indexOf(commonPrefix) != 0 ) { commonPrefix = commonPrefix.substring(0 , commonPrefix.length() - 1 ); } } return commonPrefix; } }
计算过程:(语言描述太费劲,直接拿 Replit 放示意图算了)
49. Group Anagrams
Example:
1 2 Input: strs = ["eat","tea","tan","ate","nat","bat"] Output: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) { Map<String, List<String>> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); for (String str: strs) { char [] charArray = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(charArray); String newStr = new String (charArray); if (!map.containsKey(newStr)) { map.put(newStr, new ArrayList <>()); } map.get(newStr).add(str); } List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList (map.values()); return result; } }
计算过程语言不好描述…… 但是代码挺易懂的吧,实在看不明白的话自己 debug 一下就清楚了。
118. Pascal’s Triangle
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 Input: numRows = 5 Output: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]] Input: numRows = 1 Output: [[1]]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> generate (int numRows) { if (numRows == 1 ) { return List.of(List.of(1 )); } List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(numRows); result.add(List.of(1 )); result.add(List.of(1 ,1 )); for (int row = 2 ; row < numRows; row++) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(row + 1 ); list.add(1 ); int previousRow = row - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < result.get(previousRow).size() - 1 ; i++) { int sum = result.get(previousRow).get(i) + result.get(previousRow).get(i + 1 ); list.add(sum); } list.add(1 ); result.add(list); } return result; } }
27. Remove Element
Example:
1 2 3 4 Input: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3 Output: 2, nums = [2,2,_,_] Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2. It does not matter what you leave beyond the returned k (hence they are underscores).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int removeElement (int [] nums, int val) { int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != val) { nums[count] = nums[i]; count++; } } return count; } }
929. Unique Email Addresses
Example:
1 2 3 Input: emails = ["test.email+alex@leetcode.com","test.e.mail+bob.cathy@leetcode.com","testemail+david@lee.tcode.com"] Output: 2 Explanation: "testemail@leetcode.com" and "testemail@lee.tcode.com" actually receive mails.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int numUniqueEmails (String[] emails) { HashSet<String> uniqueEmails = new HashSet <>(); for (String email : emails) { String sanitizedEmail = "" ; int indexOfPlusSign = email.indexOf("+" ); int indexOfAtSign = email.indexOf("@" ); if (indexOfPlusSign > 0 ) { sanitizedEmail += email.substring(0 , indexOfPlusSign); } else { sanitizedEmail += email.substring(0 , indexOfAtSign); } sanitizedEmail = sanitizedEmail.replace("." , "" ); sanitizedEmail += email.substring(indexOfAtSign); uniqueEmails.add(sanitizedEmail); } return uniqueEmails.size(); } }
205. Isomorphic Strings
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 Input: s = "paper", t = "title" Output: true Input: s = "foo", t = "bar" Output: false
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public boolean isIsomorphic (String s, String t) { if (s.length() != t.length()) { return false ; } HashMap<Character, Character> map = new HashMap (s.length()); for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length(); i++) { if (map.containsValue(t.charAt(i))) { continue ; } map.put(s.charAt(i), t.charAt(i)); } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { Character ch = map.get(s.charAt(i)); sb.append(ch); } return sb.toString().equals(t); } }
347. Top K Frequent Elements
Example:
1 2 Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 Output: [1,2]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { if (nums.length == k) { return nums; } return Arrays .stream(nums) .boxed() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(num -> num, Collectors.summingInt(num -> 1 ))) .entrySet() .stream() .sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue((a, b) -> Integer.compare(b, a))) .limit(k) .mapToInt(e -> e.getKey()) .toArray(); } }
还写 (chao) 了一个不用 stream,纯手工拿 entry set 做比较的解法,因过于丑陋,就不贴在这了,submission 在这里 。
128. Longest Consecutive Sequence
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4. Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] Output: 9 Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Therefore its length is 9.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } Arrays.sort(nums); int longestStreak = 1 ; int currentStreak = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1 ]) { if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] + 1 ) { currentStreak++; } else { longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak); currentStreak = 1 ; } } } return Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak); } }
125. Valid Palindrome
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Input: s = "A man, a plan, a canal: Panama" Output: true Explanation: "amanaplanacanalpanama" is a palindrome. Input: s = " " Output: true Explanation: s is an empty string "" after removing non-alphanumeric characters. Since an empty string reads the same forward and backward, it is a palindrome.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { String str = s.replaceAll("[\\W]|_" , "" ); str = str.toLowerCase(); String reversed = new StringBuilder (str).reverse().toString(); return str.equals(reversed); } }
但是很显然,这个偷鸡解法并不是 two pointers 这个分类想要的,所以另一个解法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { String str = s.replaceAll("[\\W]|_" , "" ); str = str.toLowerCase(); char [] chars = str.toCharArray(); int middle = chars.length / 2 ; int head = 0 ; int tail = chars.length - 1 ; while (head < middle) { if (chars[head] != chars[tail]) { return false ; } head++; tail--; } return true ; } }
1. Two Sum
Example:
1 2 3 Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 Output: [0,1] Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int complement = target - nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(complement)) { return new int [] { map.get(complement), i }; } map.put(nums[i], i); } throw new IllegalArgumentException ("No solution found" ); } }
计算过程:
i = 0,nums[i] = 2,complement = 9 - 2 = 7,map 的 key 里面找不到 7,所以 map.put(2, 0)i = 1,nums[i] = 7,complement = 9 - 7 = 2,map 的 key 里面有 2,即 nums[i] + nums[map.get(2)] = 9,返回 [map.get(2), nums[i]] 即 [0, 1]
Example:
1 2 3 Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 Output: [1,2] Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore, index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] numbers, int target) { int low = 0 ; int high = numbers.length - 1 ; while (low < high) { int sum = numbers[low] + numbers[high]; if (sum == target) { return new int [] {low + 1 , high + 1 }; } else if (sum < target) { ++low; } else { --high; } } return new int [] {-1 , -1 }; } }
15. 3Sum
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] Explanation: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0. nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0. nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0. The distinct triplets are [-1,0,1] and [-1,-1,2]. Notice that the order of the output and the order of the triplets does not matter.
一种解法是,类似 Two Sum II,取一个基准数,然后用 Two Sum II 的方法找基准数右边符合要求的两个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length && nums[i] <= 0 ; ++i) { if (i == 0 || nums[i - 1 ] != nums[i]) { twoSumII(nums, i, result); } } return result; } private void twoSumII (int [] nums, int i, List<List<Integer>> result) { int low = i + 1 ; int high = nums.length - 1 ; while (low < high) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[low] + nums[high]; if (sum < 0 ) { ++low; } else if (sum > 0 ) { --high; } else { result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[low], nums[high])); low++; high--; while (low < high && nums[low] == nums[low - 1 ]) { ++low; } } } } }
但是,如果题目不允许改变 nums 数组呢?那么可以这样解,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { Set<List<Integer>> result = new HashSet <>(); Set<Integer> duplicates = new HashSet <>(); Map<Integer, Integer> seen = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!duplicates.add(nums[i])) { continue ; } for (int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++) { int complement = -(nums[i] + nums[j]); if (seen.containsKey(complement) && seen.get(complement) == i) { List<Integer> triplet = Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], complement); Collections.sort(triplet); result.add(triplet); } seen.put(nums[j], i); } } return new ArrayList <>(result); } }
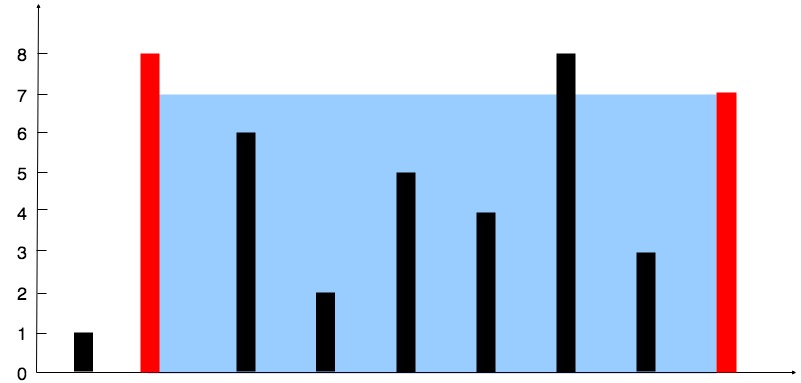
11. Container With Most Water
Example:
1 2 3 Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int maxArea (int [] height) { int max = 0 ; int left = 0 ; int right = height.length - 1 ; while (left < right) { int ht = Math.min(height[left], height[right]); int water = right - left; int volume = ht * water; max = Math.max(max, volume); if (height[left] < height[right]) { left++; } else { right--; } } return max; } }
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Example:
1 2 3 4 Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4] Output: 5 Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5. Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { if (prices.length < 2 ) { return 0 ; } int buyPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int overallProfit = 0 ; int profitIfSoldToday = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < prices.length; i++) { if (prices[i] < buyPrice) { buyPrice = prices[i]; } profitIfSoldToday = prices[i] - buyPrice; if (overallProfit < profitIfSoldToday) { overallProfit = profitIfSoldToday; } } return overallProfit; } }
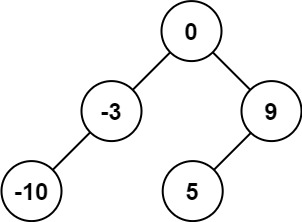
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Example:
1 2 Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return builder(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } private TreeNode builder (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (left > right) { return null ; } int middle = (left + right) / 2 ; TreeNode rootNode = new TreeNode (nums[middle]); rootNode.left = builder(nums, left, middle - 1 ); rootNode.right = builder(nums, middle + 1 , right); return rootNode; } }
思路就是递归 + 二分,或许还有些分治思想?先找见根节点,然后把数组左右分成两半,在递归里面再重复这样的操作,直到只有一个根节点,也就是最下面的叶子节点。最后往上组装。
146. LRU Cache
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Input ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] Output [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4] Explanation LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // return 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found) lRUCache.get(3); // return 3 lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
解题思路:
LRU Cache,即 Least Recently Used Cache,其运作机理是,如果在 cache 已满的时候添加新的记录,那么要先删掉其中最不常用的记录,然后添加新的记录。
我们可以用双向链表来实现这个效果,越靠近链表头,就代表这个元素越常被用到;反之越靠近链表尾,这个元素就越不常用,链表尾的前一个元素也将是在 cache 满了之后被删掉的那个元素。
那么首先需要创建一个类 Node,代表双向链表中的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Node { Node next; Node prev; int key; int value; public Node (int key, int value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } }
这时候就可以初始化 LRUCache 这个类的结构了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class LRUCache { private final Node head = new Node (0 , 0 ); private final Node tail = new Node (0 , 0 ); private final Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap <>(); private final int capacity; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; } }
接下来先实现 get 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public int get (int key) { if (!map.containsKey(key)) { return -1 ; } Node node = map.get(key); Node nodeNext = node.next; Node nodePrev = node.prev; nodePrev.next = nodeNext; nodeNext.prev = nodePrev; Node headNext = head.next; node.next = headNext; node.prev = head; headNext.prev = node; head.next = node; return node.value; }
接下来实现 put 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { Node node = map.remove(key); Node nodeNext = node.next; Node nodePrev = node.prev; nodePrev.next = nodeNext; nodeNext.prev = nodePrev; } if (map.size() == capacity) { Node leastRecentUsedNode = tail.prev; map.remove(leastRecentUsedNode.key); leastRecentUsedNode.prev = tail; tail.prev = leastRecentUsedNode.prev; } Node newNode = new Node (key, value); map.put(key, newNode); Node headNext = head.next; newNode.prev = head; newNode.next = headNext; headNext.prev = newNode; head.next = newNode; }
可见新增节点和删除节点操作的代码是经常重复的,所以抽成两个单独的方法。最后完整的解题代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class LRUCache { private final Node head = new Node (0 , 0 ); private final Node tail = new Node (0 , 0 ); private final Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap <>(); private final int capacity; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; } public int get (int key) { if (!map.containsKey(key)) { return -1 ; } Node node = map.get(key); remove(node); insert(node); return node.value; } public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.containsKey(key)) { remove(map.get(key)); } if (map.size() == capacity) { remove(tail.prev); } insert(new Node (key, value)); } private void remove (Node node) { map.remove(node.key); node.prev.next = node.next; node.next.prev = node.prev; } private void insert (Node node) { map.put(node.key, node); Node headNext = head.next; node.prev = head; node.next = headNext; headNext.prev = node; head.next = node; } public class Node { Node next; Node prev; int key; int value; public Node (int key, int value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } } }
9. Palindrome number
Example:
1 2 3 Input: x = 121 Output: true Explanation: 121 reads as 121 from left to right and from right to left.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (int x) { if (x < 0 ) { return false ; } int input = x; int reversedNum = 0 ; while (x != 0 ) { reversedNum = reversedNum * 10 + x % 10 ; x = x / 10 ; } if (reversedNum > Integer.MAX_VALUE || reversedNum < Integer.MIN_VALUE) { return false ; } return input == reversedNum; } }
计算过程:
x = 121,reversedNum = 0;reversedNum = reversedNum * 10 + x % 10 = 0 + 1 = 1;x = x / 10 = 121 / 10 = 12x = 12,reversedNum = 1;reversedNum = reversedNum * 10 + x % 10 = 10 + 2 = 12;x = x / 10 = 12 / 10 = 1x = 1,reversedNum = 12;reversedNum = reversedNum * 10 + x % 10 = 120 + 1 = 121;x = x / 10 = 1 / 10 = 0input == reversedNum => 121 == 121 => true
写到这想到还有个粗暴解法,把数字当成字符串,翻转一下然后比较两个字符串是不是一样不就行了,做什么数学题?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (int x) { String inputString = Integer.toString(x); String reversedString = new StringBuilder (inputString).reverse().toString(); return inputString.equals(reversedString); } }
多清爽,三行完事还不烧脑子。
13. Roman to Integer
Example:
1 2 3 Input: s = "MCMXCIV" Output: 1994 Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int romanToInt (String s) { final HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(7 ); map.put('I' , 1 ); map.put('V' , 5 ); map.put('X' , 10 ); map.put('L' , 50 ); map.put('C' , 100 ); map.put('D' , 500 ); map.put('M' , 1000 ); final String sanitized = s .replace("IV" , "IIII" ) .replace("IX" , "VIIII" ) .replace("XL" , "XXXX" ) .replace("XC" , "LXXXX" ) .replace("CD" , "CCCC" ) .replace("CM" , "DCCCC" ); final char [] chars = sanitized.toCharArray(); int result = 0 ; for (char aChar : chars) { result += map.get(aChar); } return result; } }
计算过程:
MCMXCIV(1994) => M CM XC IV(1000 900 90 4) => M DCCC LXXXX IIII从头到尾遍历 MDCCCLXXXXIIII 中每个字符,去 map 里面找对应的阿拉伯数字,加起来就完事了
一开始做的时候愁死我了,没有左减格式的数字没啥难度,想破脑袋也没想到怎么处理左减,抄答案发现还能这么玩,属实打开思路了。
252. Meeting Rooms
Given an array of meeting time intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], determine if a person could attend all meetings.
Example:
1 2 Input: intervals = [[0,30],[5,10],[15,20]] Output: false
Easy 级别的题,思路很简单,先把会议安排按照开始时间升序排列,然后比较下一场会议的开始时间是否小于上一场会议的结束时间,是的话就说明这个人无法参加全部会议。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public boolean canAttendMeetings (int [][] intervals) { if (intervals.length <= 1 ) { return true ; } Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); int lastEndTime = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { int currentBeginTime = intervals[i][0 ]; if (currentBeginTime < lastEndTime) { return false ; } lastEndTime = intervals[i][1 ]; } return true ; } }
253. Meeting Rooms II
Given an array of meeting time intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], return the minimum number of conference rooms required.
Example:
1 2 Input: intervals = [[0,30],[5,10],[15,20]] Output: 2
这道题要用到优先队列,具体算法见注释。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public int minMeetingRooms (int [][] intervals) { if (intervals.length <= 1 ) { return intervals.length; } PriorityQueue<Integer> allocator = new PriorityQueue <>( intervals.length, (a, b) -> a - b ); Arrays.sort( intervals, (a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); allocator.add(intervals[0 ][1 ]); for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { if (intervals[i][0 ] >= allocator.peek()) { allocator.poll(); } allocator.add(intervals[i][1 ]); } return allocator.size(); } }
655. Print Binary Tree 抄答案 Java Easy Solution - shawonnirob16
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class Solution { public List<List<String>> printTree (TreeNode root) { List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList <>(); int height = getHeight(root); int row = height + 1 ; int column = (int ) Math.pow(2 , height + 1 ) - 1 ; for (int k = 0 ; k < row; k++) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < column; i++) { list.add("" ); } result.add(list); } int left = 0 ; int right = column - 1 ; int level = 0 ; fill(result, left, right, level, root); return result; } private int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return -1 ; } int left = getHeight(root.left); int right = getHeight(root.right); return 1 + Math.max(left, right); } private void fill ( List<List<String>> result, int left, int right, int level, TreeNode root ) { if (root == null ) { return ; } int middle = left + (right - left) / 2 ; result.get(level).set(middle, String.valueOf(root.val)); fill(result, left, middle - 1 , level + 1 , root.left); fill(result, middle + 1 , right, level + 1 , root.right); } }